Seismology is the scientific study of earthquakes and the propagation of elastic waves through the Earth. When an earthquake occurs, it releases a tremendous amount of energy that radiates outward from the source, or focus, in the form of seismic waves. These seismic waves are the primary tools used by seismologists to study the Earth's interior. Understanding the different types of seismic waves is crucial for interpreting seismic data and gaining insights into the Earth's composition and structure.
Types of seismic waves
Seismic waves can be broadly classified into two main categories: body waves and surface waves. Body waves travel through the Earth's interior, while surface waves propagate along the Earth's surface. Each type of wave has unique characteristics that influence its behavior and the information it provides about the Earth.
Body waves
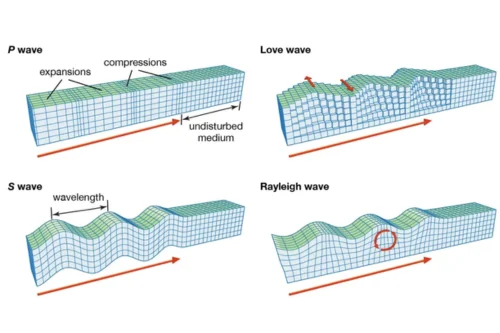
Body waves are further subdivided into two types: P waves and S waves.
- S Waves (Secondary Waves): S waves are slower than P waves and can only travel through solid materials. They are transverse waves, meaning that the particle motion is perpendicular to the direction of wave propagation.
- S waves are sometimes referred to as shear waves. Because the Earth's outer core is liquid, S waves cannot pass through it, providing valuable information about the Earth's internal structure. P Waves (Primary Waves): P waves are the fastest type of seismic wave and can travel through both solid and liquid materials. They are longitudinal waves, meaning that the particle motion is parallel to the direction of wave propagation. P waves are often compared to sound waves as they involve a push-pull motion of particles. Due to their high velocity, P waves are the first to arrive at a seismic station following an earthquake.
Surface Waves
Surface waves travel along the Earth's surface and are generally slower than body waves. There are two main types of surface waves: Love waves and Rayleigh waves.
- Love Waves: Love waves are horizontal shear waves that cause the ground to move from side to side perpendicular to the direction of wave propagation. Love waves do not have a vertical component of motion. They are named after A.E.H. Love, a British mathematician who developed the mathematical theory for these waves.
- Rayleigh Waves: Rayleigh waves are surface waves that produce a rolling motion of the ground. The particle motion of a Rayleigh wave is elliptical and retrograde, meaning that particles move in a counterclockwise direction. Rayleigh waves are named after Lord Rayleigh, who predicted their existence theoretically.
How are recorded seismic waves? Seismographs and sismograms
Seismic waves are recorded by instruments called seismographs. A seismograph produces a seismogram, which is a graphical representation of ground motion. Seismograms provide valuable information about the characteristics of seismic waves, such as amplitude, frequency, and arrival time. By analyzing seismograms from multiple stations, seismologists can determine the location and magnitude of an earthquake, as well as the properties of the Earth's interior.
Determining earth’s structure
The study of seismic waves has played a pivotal role in determining the Earth's internal structure. Seismic wave travel times and the behavior of waves at different depths provide constraints on the composition and physical properties of the Earth's layers. For example, the observation that S waves cannot pass through the outer core led to the conclusion that it is liquid.
Seismic tomography
Seismic tomography is a powerful technique used to create high-resolution images of the Earth's interior. It involves analyzing the travel times of seismic waves from numerous earthquakes to map variations in the Earth's composition and temperature. By measuring the time it takes for seismic waves to travel from the source to a network of seismic stations, scientists can infer the properties of the material through which the waves pass.
Types of seismic tomography
- Global Tomography: This technique uses seismic waves from large earthquakes recorded by a global network of seismic stations to create images of the entire Earth's mantle and core.
- Regional Tomography: Regional tomography focuses on smaller-scale structures within the Earth's crust and upper mantle. It is particularly useful for studying active tectonic regions and volcanic areas.
- Local Tomography: Local tomography is used to investigate shallow subsurface structures, such as faults, magma chambers, and groundwater reservoirs.
Applications of seismic tomography
- Mapping subducting slabs: Seismic tomography can track the descent of subducting tectonic plates into the Earth's mantle, providing insights into the recycling of Earth's material.
- Identifying mantle plumes: Mantle plumes are narrow columns of hot rock that rise from the Earth's core, driving volcanic activity. Seismic tomography can help locate and study mantle plumes.
- Exploring the core-mantle boundary: The core-mantle boundary is a region of significant chemical and physical contrast. Seismic tomography can reveal details about the structure and dynamics of this boundary.
- Monitoring volcanic activity: By imaging the subsurface beneath volcanoes, seismic tomography can help detect changes in magma reservoirs and assess the potential for eruptions.
Seismic waves are essential tools for understanding the Earth's interior and studying earthquakes. The four main types of seismic waves – P waves, S waves, Love waves, and Rayleigh waves – each have unique characteristics and provide complementary information about the Earth's structure. By analyzing seismic data, scientists can gain insights into the processes that shape our planet and assess seismic hazards.
To further advance our understanding of seismic waves, it is recommended to:
- Continued research: Continued research on seismic wave propagation and the development of advanced seismic imaging techniques are essential for improving our understanding of the Earth's interior.
- Global seismic networks: Expanding and improving global seismic networks will enhance our ability to monitor earthquakes and assess seismic hazards.
- Education and public awareness: Promoting public awareness of earthquakes and seismic hazards is crucial for reducing the impact of future earthquakes.
You may also be interested in

