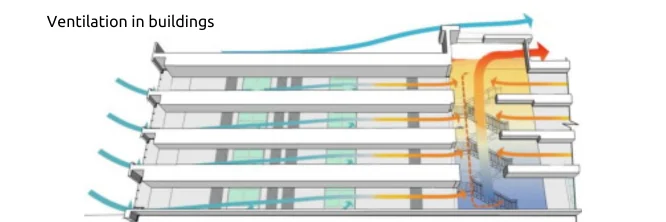
Ventilation in buildings is a critical factor in maintaining a healthy and comfortable indoor environment. It involves the process of supplying fresh air to and removing contaminated air from a space. Proper ventilation is essential for ensuring good indoor air quality, which can significantly impact the health and productivity of building occupants. This article will delve into the importance of ventilation, the causes of poor ventilation, and various methods to improve air quality within buildings.
![ventilation y buildings]()
How do you provide good ventilation in a building?
Good ventilation involves a balance between bringing in fresh outdoor air and removing contaminated air. A well-ventilated building should have a sufficient supply of ventilation air to dilute pollutants and maintain a comfortable temperature and humidity level.
Causes of poor ventilation in buildings
Several factors can contribute to poor ventilation in buildings, including:
- Airtight construction: Modern buildings are often constructed to be very airtight, which can reduce natural ventilation and trap pollutants indoors.
- Lack of mechanical ventilation: Buildings without mechanical ventilation systems may rely solely on open windows for ventilation, which can be ineffective, especially in extreme weather conditions.
- Inadequate fan operation: Exhaust fans and ceiling fans may not be sized or operated correctly to effectively remove contaminated air.
- Poor ventilation design: Buildings with poorly designed ventilation systems may have inadequate airflow or uneven distribution of fresh outdoor air.
Three methods used to ventilate a building
There are three primary methods used to ventilate a building:
- Natural ventilation: This method relies on wind pressure and temperature differences to drive airflow through open windows and doors. While it is energy-efficient, natural ventilation can be unpredictable and may not be sufficient in all climates.
- Mechanical ventilation: Mechanical ventilation systems use fans to force air into and out of a building. These systems can provide controlled ventilation and can be used to remove contaminated air and introduce fresh outdoor air even in adverse weather conditions.
- Hybrid ventilation: Hybrid ventilation combines elements of natural and mechanical ventilation. This approach can provide a more flexible and efficient solution for many buildings.
What is the preferred method to ventilate a large building?
For large buildings, mechanical ventilation is often the preferred method. It allows for precise control of ventilation air volume and distribution, ensuring adequate ventilation in all areas of the building. Mechanical ventilation systems can also be equipped with heat recovery units to reduce energy consumption.
Factors affecting ventilation system performance
Several factors can affect the performance of a ventilation system, including:
- Airflow: The amount of ventilation air supplied to a space is measured in air changes per hour (ACH). A higher ACH rate means that the air in a space is replaced more frequently.
- Filtration: Filters remove particles from the ventilation air, improving indoor air quality.
- Humidity control: Ventilation systems can help control humidity levels by removing moisture from the indoor air.
- Carbon dioxide (CO2) levels: CO2 is a common indoor pollutant, and ventilation systems can help to reduce CO2 concentrations by diluting the air with fresh outdoor air.
Benefits of good ventilation
Good ventilation offers numerous benefits, including:
- Improved indoor air quality: By removing contaminated air and introducing fresh outdoor air, ventilation can reduce the concentration of pollutants such as allergens, dust, and chemicals.
- Reduced risk of illness: Good ventilation can reduces the risk of respiratory infections and other health problems.
- Increased productivity: Studies have shown that good indoor air quality can improve cognitive function and productivity.
- Enhanced comfort: Ventilation can help to maintain a comfortable temperature and humidity level, improving occupant comfort.
Ventilation and energy efficiency
Effective ventilation is crucial for maintaining a healthy indoor environment, but it can also have a significant impact on energy efficiency. Poorly designed or operated ventilation systems can lead to increased energy consumption. However, with careful planning and implementation, ventilation systems can be designed to minimize energy consumption while still providing adequate air quality.
Here are some key factors to consider when evaluating the energy efficiency of ventilation systems:
- Heat Recovery: Heat recovery systems can capture and reuse the heat or cooling energy from exhaust air to preheat or precool incoming fresh air. This can significantly reduce the energy required for heating or cooling the building.
- Demand-Controlled Ventilation (DCV): DCV systems adjust the ventilation rate based on occupancy and indoor air quality levels. This can help to avoid over-ventilating the building, reducing energy consumption.
- Fan Efficiency: High-efficiency fans can reduce energy consumption while still providing adequate airflow.
- Airtightness: A well-sealed building envelope can reduce energy loss through infiltration and exfiltration, improving the overall energy efficiency of the building.
Specific ventilation technologies
In addition to the factors mentioned above, there are several specific ventilation technologies that can improve energy efficiency:
- Radiant Heating and Cooling: Radiant heating and cooling systems can provide localized heating or cooling, allowing for more precise temperature control and potentially reducing overall energy consumption.
- Decentralized Ventilation: Decentralized ventilation systems, such as individual room ventilation units, can provide targeted ventilation where it is needed, reducing energy consumption compared to centralized systems.
- Natural Ventilation: In some climates, natural ventilation can be an effective and energy-efficient way to provide fresh air. However, it is important to carefully consider factors such as wind direction, temperature differences, and building orientation to ensure adequate ventilation.
By carefully considering these factors and implementing appropriate ventilation technologies, building owners and operators can improve energy efficiency and reduce operating costs while maintaining a healthy indoor environment.
Ventilation in buildings plays a crucial role in maintaining a healthy and comfortable indoor environment. By understanding the factors that affect indoor air quality and the different methods of ventilation, building owners and occupants can make informed decisions to improve the quality of the air they breathe.
Recommendations
- Regularly inspect and maintain ventilation systems.
- Consider using natural ventilation systems when possible, such as opening windows on mild days.
- Install high-efficiency particulate air (HEPA) filters to remove fine particles from the ventilation air.
- Monitor indoor air quality using CO2 monitors and other sensors.
- Educate building occupants about the importance of ventilation and how to properly use ventilation controls.
By following these recommendations, building owners and occupants can create healthier and more comfortable indoor environments.
Do you want to find interesting related content?